The ideal: forming a proper fillet
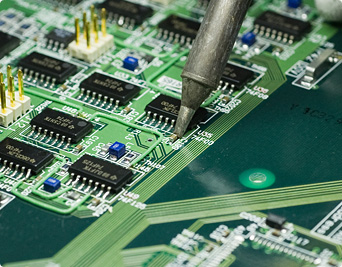
Soldering chip components of under 1 mm in size. The heating temperature is regulated by minutely adjusting the angle at which the soldering iron makes contact.
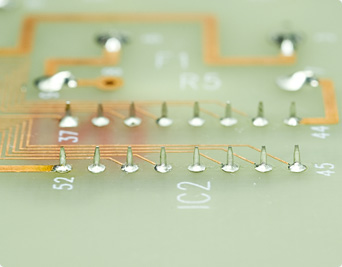
Fillets formed by soldering.
Manual soldering is a metal bonding operation that involves forming a junction region (consisting of an alloy layer) between a lead on an electronic component and a land on a PCB by spreading solder over them both.
With optimal soldering, the solder will spread out like the base of a mountain and the shape of the lead will be barely perceptible. This configuration is known as a "fillet." If the lead and the land are heated to the same temperature and just the right amount of solder is flowed on to cover them both completely, a perfect fillet will be formed.
There are chip-type electronic components that measure as little as 1.0 mm x 0.5 mm. With ICs, soldering is performed on their surrounding leads. The spacing between these leads is as little as 0.5 mm. This soldering of minute electronic components is known as "micro-soldering."

