Super Resolution Microscope N-STORM
Achieving a resolution 10 times greater than a conventional optical microscope enables molecular level understanding

STochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy (STORM) reconstructs a super resolution fluorescent image by combining precisely localized information of each fluorophore detected within a complex microscope specimen. N-STORM applies high-accuracy multi-channel molecular localization and reconstruction in 3 dimensions taking full advantage of Nikon's powerful Ti-E inverted microscope, realizing super resolution of 10 times (approx. 20nm laterally) greater than conventional microscopes. This powerful technology can bring to view nanoscopic molecular interactions opening new worlds of understanding.
Super resolution at 10 times (approx. 20nm laterally) greater than conventional optical microscopes
N-STORM utilizes highly accurate localization information (2D or 3D) of 1000's of discrete fluorophor moleculess within a microscope specimen to create breathtaking "super-resolution" images, exhibiting spatial resolution 10 times greater than conventional optical microscopes.
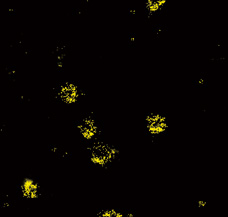
- Single color STORM image of a clathrin-coated pit in a mammalian cell labeled with Cy3-Alexa647
Objective: CFI Apo TIRF 100x oil (NA 1.49)

N-STORM can uniquely generate greater than 10 times standard optical resolution axially as well (approx. 50nm)
In addition to lateral super-resolution, N-STORM utilizes proprietary methods to achieve a 10 fold enhancement in axial resolution, effectively providing 3D information at a nanoscopic scale.
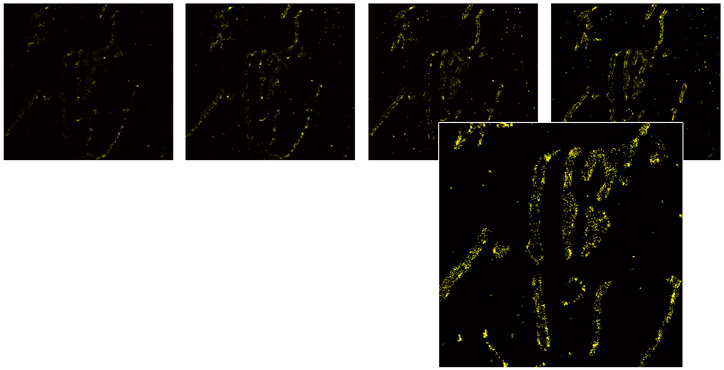
- Single color 3D-STORM image of mitochondria in a mammalian cell labeled with Cy3-Alexa647
Objective: CFI Apo TIRF 100x oil (NA 1.49)
Z step: 50nm
Multi-color imaging using various fluorescent probes
Multi-color super resolution imaging is possible by cleverly combining various "activator" and "reporter" probes. This makes it possible to gain critical insight into the co-localization and interaction of multiple proteins at the molecular level.
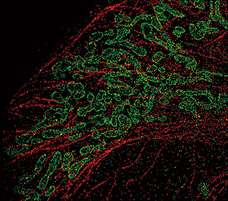
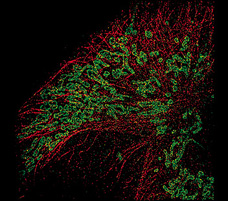
- Dual color STORM image of microtubule (Alexa405-Alexa647) and mitochondria (Cy3-Alexa647) in a mammalian cell.
Objective: CFI Plan Apo VC 100x oil (1.40)
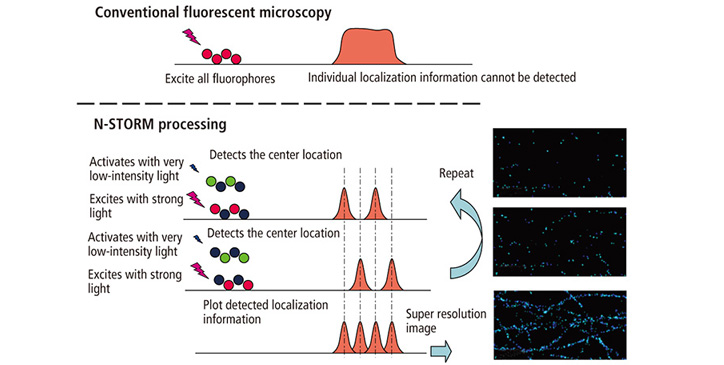
The Principle of N-STORM (STochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy)
STochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy (STORM) reconstructs a super resolution image by combining the high-accuracy localization information of each fluorophore in 3 spatial dimensions and multiple colors
N-STORM uses stochastic activation of relatively small numbers of fluorophor molecules using very low-intensity light. This low-level stochastic "activation" of discrete molecules enables high precision Gaussian fitting of each laterally. Additionally, taking advantage of an induced astigmatism via the special 3D-STORM optics, N-STORM localizes each molecule axially. Computationally combining molecular coordinates in 3 dimensions results in high contrast 3D images of the nanoscopic world with molecular specificity.
Dedicated fluorescent dyes
N-STORM uses dedicated fluorescent dye pairs containing an "activator" (relatively short wavelength excitation) and a "reporter" (relatively long wavelength excitation), which enables various color combinations, facilitating true multi-channel super resolution.
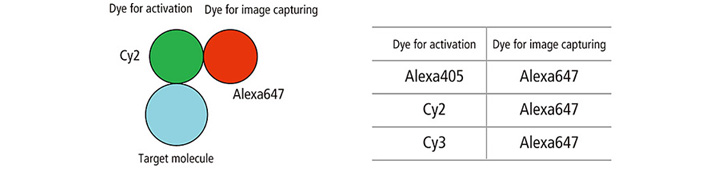
- A dye for N-STORM consists of a shorter-wavelength dye for activation and a longer-wavelength dye for image capturing. Creation of two color super resolution images is possible with pairs of dye.

