Inverted Research Microscope ECLIPSE Ti
- Stable time-lapse imaging with automatic focus correction system
- High-speed motorized control and acquisition
- High-quality phase contrast images using high NA lenses
- Advanced integration with peripherals via intelligent software
- Motorized laser TIRF illumination unit
- Photo activation illumination unit
- TIRF photo activation
- Multiport design with a maximum of five imaging ports
- Three models for a wide range of applications
The inverted microscope series at the center of bioscience's most advanced imaging techniques

Scientists have overcome many live cell imaging challenges using advanced techniques such as TIRF, confocal, FRET, photo activation and microinjection. At the center of all this is the Eclipse Ti, a powerful system that provides instant access to all these methods plus revolutionary Nikon CFI60 optics. Available in three models, the Ti series offers improved system speeds, increased flexibility and efficient multi-mode microscopy as part of a fully-integrated microscope system that is ideal for high-end research and live cell imaging.
Stable time-lapse imaging with automatic focus correction system
The Ti-E comes with a unique Perfect Focus System (PFS) that automatically corrects focus drift in real time during a prolonged period of time-lapse imaging.
Focus drift resulting from a temperature drop when reagents are added is instantaneously corrected and the rapid change of cells can be captured.
The incorporation of the PFS in the nosepiece unit saves space and allows two optical component levels to be attached simultaneously utilizing stratum structure.
EB1 and tubulin in the cortex of Physcomitrella patens moss
Images were acquired on a spinning disk confocal with a Plan Apochromat VC 100x 1.4 NA lens at the Marine Biological Laboratory.
Movie courtesy of: Drs. Jeroen de Keijzer and Marcel Janson, Wageningen University, and Dr. Gohta Goshima, Nagoya University.
Concept of the Perfect Focus System
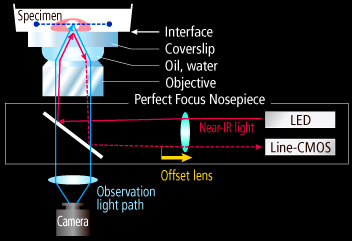
The diagram shows the case when an immersion type objective is used. A dry type objective is also available.
Correction to focus drift when reagents are added
With PFS
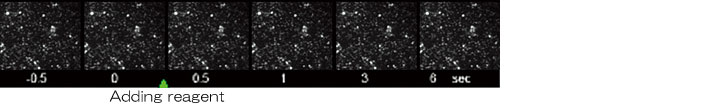
Without PFS
Maintaining focus at greater depths
Focus drift can now be corrected in a broader range of Z-axis planes than ever before. Maintaining focus at greater distances from the objective lens and at greater depths within the specimen is also possible.
In addition, PFS's focus drift correction range has been widened, resulting in more reliable and stable data.
Because PFS can maintain focus at greater depths within the specimen, whole images of intersegmental vessels sprouting upward from the dorsal aorta are clearly captured. Shown in the three channels are three different timepoint volumes (red: 0 mins, green: 110 mins, blue: 240 mins).
Specimen: vasculature of a zebrafish embryo (95-186 µm away from the coverslip).
Movie courtesy of: Dr. Robert Fischer, Marine Biological Laboratory
Improved performance in broader wavelength range

By now employing 870nm wavelength for the coverglass interface detection, near-infrared fluorescence dyes including Cy5.5 can be used. Nikon offers two PFS models, one for UV-visible wavelength imaging and one for multiphoton imaging. The multiphoton model can correct for focus drift even when imaging with wavelengths ranging from 880-1300 nm.
Compatible with plastic dishes and well plates
In addition to glass bottom dishes, plastic dishes can be used with PFS. The system is especially suited to high-throughput screening applications that involve multi-well plates.
High-speed motorized control and acquisition
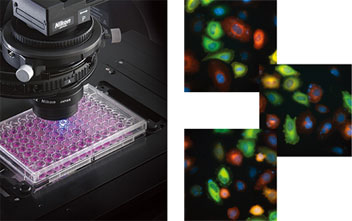
Multipoint snapshots of HeLa cells transiently expressing Venus-tubulin and mCherry-actin and stained with Hoechst33342 and DiD. (All in pseudo-color)
Photos courtesy of: Kenta Saito and Takeharu Nagai, Research Institute for Electronic Science, Hokkaido University
The operational speeds of motorized components such as the nosepiece, fluorescence filters and stage have been greatly enhanced, allowing high-speed screening image capture during multi-dimensional experiments. Faster device movement and image acquisition reduce overall light exposure and subsequent photo-toxicity, leading to more meaningful data. The digital Controller Hub significantly increases motorized accessory speed by reducing communication overhead time between components, boosting total operation speed.
High-quality phase contrast images using high NA lenses
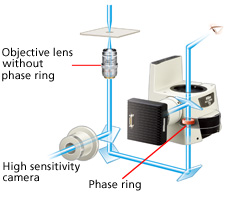
The revolutionary external phase contrast unit incorporates a phase ring and allows the use of high NA objective lenses without a phase ring for phase contrast observation. Because there is no light loss due to a phase ring, bright "full intensity" fluorescence images as well as high-resolution phase contrast images can be captured using the same objective lens.
Advanced integration with peripherals via intelligent software
Nikon's comprehensive imaging software NIS-Elements provides an integrated control of the microscope, cameras, components and peripherals. The intuitive GUI and efficient workflow make the programming of automated imaging sequences up to 6D (X, Y, Z, time, wavelength, multipoint) easy to perform.
6D time-lapse imaging system
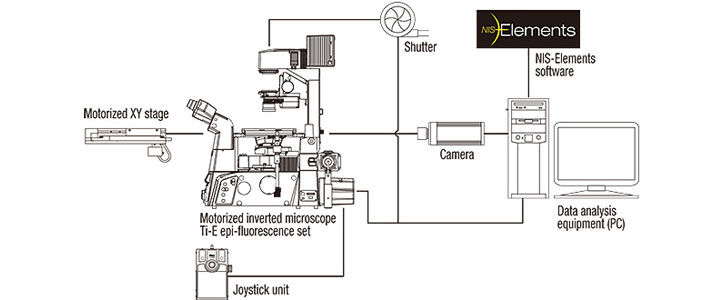
Motorized laser TIRF illumination unit

The motorized laser TIRF illuminator was developed for use with Ti-E and Ti-U. The laser incident angle can be easily stored and reproduced with a single touch of the control pad button. This enables alternate time-lapse recording between multi-wavelength TIRF and epi-fluorescence images.
Time-lapse imaging by switching TIRF and epi-fluorescence observation
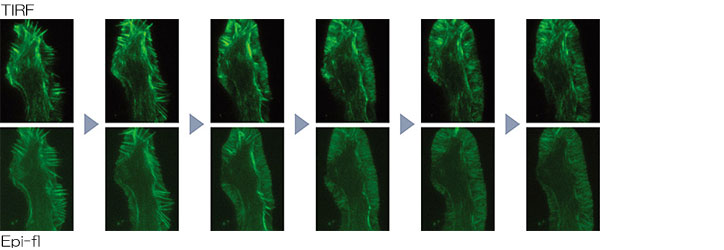
NG108 cell: Growth cone stained with EGFP-fascin
Photos courtesy of: Satoe Ebihara, Kaoru Katoh, The National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST)
Photo activation illumination unit

The Ti-E and Ti-U feature a specialized photo activation illuminator that allows fluorescent time-lapse observation of dynamic events following photo activation or photo conversion.

Photo activation of PA-GFP in a living mammalian cell by 405nm laser irradiation
Photos courtesy of: Tomoki Matsuda and Takeharu Nagai, Research Institute for Electronic Science, Hokkaido University
TIRF photo activation

With the integration of the laser TIRF illuminator and photo activation unit, both functions are now combined in one microscope. The user can switch between the two functions with ease.
Multiport design with a maximum of five imaging ports

Use of an optional back port enables multiple wavelength FRET imaging with multiple cameras. Moreover, by adding an eyepiece tube base unit with a side port, a maximum of five imaging ports* including left, right and bottom ports are available. (*With Ti-E/B model with bottom port)
Three models for a wide range of applications
Ti-E

The flagship model that is fully motorized for automated multimode image techniques and acquisition
(A model with a bottom port is also available.)
Ti-U

The universal model with the potential for diverse laser illuminators and motorized components
(A model with a bottom port is also available.)
Ti-S

The basic model that can be dedicated to specific tasks
