1. Precision in component manufacturing determines product performance
In our everyday lives we see a huge range of industrial products all around us. Most of them have been assembled from a large number of components. The manufacture of every component requires high-precision machining in order for a product to effectively function.

Recently, hybrid and electric vehicles have become increasingly popular in the automobile market. The engine noise of such vehicles has been drastically reduced. Instead, gear noises are now more audible, which has brought demands for extremely high precision in gear manufacturing.
Before the era of hybrid and electric vehicles, gear noises were drowned out by louder engine noise and were not recognized as a problem. Now, as these vehicles realize quieter running, gear sounds have become more prominent as a major factor of automotive noise. Enhancing precision in automotive gear manufacturing reduces gear noise, resulting in much quieter running on the road, while realizing smooth power transmission and extending fuel efficiency. Higher precision in gear manufacturing leads to dynamic improvements in performance and quality as a whole of the final product.
At manufacturing sites, demands are high for precision that meets the specifications stipulated in the original design. In order to achieve the required results, high-precision measurement technology is essential, along with highly advanced manufacturing technologies.
2. 3D measurements of dimensions and shape
For the inspection of machined components, manufacturers formerly utilized a tactile metrology device to measure dimensions by directly touching samples with a touch-probe sensor. However, for effective measurement of a smooth surface such as a camera body it is necessary to collect information from tens to hundreds of thousands of contact points. In particular, gear wheels for automobiles have shapes very carefully developed from various parameters such as quiet motion, smooth gear mating, and rigid construction. Measurement of these products also demands time. The shorter the time taken, the fewer the contact points will be, resulting in less information collected. Measurement that obtains less information is insufficient and inaccurate.
Eventually, non-contact 3D metrology devices were developed to replace the tactile metrology model. These devices measure shapes by projecting laser beams onto test subjects and collecting as much point-cloud data as possible. However, this device only the precision of tens to hundreds of micrometers and therefore was not practical for use in fields that demand single-digit micrometer, higher-precision machining.
Nikon entered here with its unique solution — the HN-6060 non-contact multi-sensor 3D metrology system — which brings together technologies developed in various sectors of the company. This non-contact multi-sensor 3D metrology system is now attracting the attention of the industry as a product that will expedite the evolution of high-precision 3D measuring technology.
This system, though designed as a non-contact device, achieves accurate, high-precision measurement equal to that of the tactile type, due to a light section sensor of Nikon's own development. Also, as it enables high-speed digital conversion of the measurement data, the system deals with 120,000 point-cloud data per second, realizing superior efficiency of measurement.
Previously, it was not easy to attain satisfactory results for the measurement of gears, even if there were no time constraints. The HN-6060, with its high-speed and high-precision measurement capacity, requires only a few minutes to undertake finely accurate measurement of overall gear shape including corners around the top and bottom of teeth.
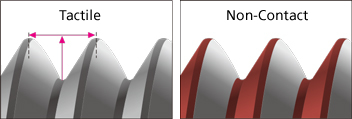
The tactile sensor measures dimensions between gear teeth, while the non-contact light sensor measures the overall shape.

HN-6060 non-contact multi-sensor 3D metrology system

Multi-sensor head comprises three types of sensor
Light section, SFF and tactile sensors work in unison to achieve optimum measurement, even in areas where a laser beam alone cannot reach or a light section sensor fails to measure due to surface reflections.
3. High-rigidity, five-axis control design enables the world's highest precision*
At the core of the HN-6060's high-precision technologies is a light section sensor. This device was developed by integrating various Nikon technologies, achieving a high micrometer level of precision, the world's highest* in the field of current non-contact 3D metrology devices.
- *As of June 30, 2011, Nikon data
However, the light section sensor alone allows only linear section scanning, and is unable to project light at blind spots or certain points obscured by elevations, depressions or curves of the test subject's surface, resulting in failure to achieve optimum precision measurement. In addition, with the light section sensor design, external light may interfere with measurement. In order to overcome these problems, the HN-6060 employs a high-rigidity, five-axis control design, enabling scanning at an ideal angle for the target position, and attaining maximum performance.
Three-axis movement of the sensor head, right and left, forward and backward, and up and down, as well as free rotation of the two-axis rotary table, enables the test subject to direct sides for easy measurement by the sensor head. The system employs an exclusive algorithm, which assures high-precision measurement by five-axis synchronized sensor control and optimized sequential compensation, while moving a test subject of complicated shape to the ideal position for measurement.

Comparison of the shape of a hypoid gear in the display
High-rigidity, five-axis control design
Three-axis sensors and a two-axis rotary table enable measurement of test subjects from various perspectives, synchronized in motion.
The HN-6060 features a diverse range of Nikon technologies such as a light section sensor, high-speed digital conversion processor, and five-axis sensor control device, achieving high-precision test subject measurement with the utmost efficiency and accuracy. There should be many other ways to apply these technologies in the future to widen use of the HN-6060, for example, to analyze prototypes of products, improve manufacturing processes, undertake reverse engineering, and utilize in car drive simulation tests; or to measure soft plastic molds that may suffer distortion, or errors in measurement, caused by contact pressure.

